Web Service Actions - Rest Action
Invokes a REST service with support for SSL encryption, security certificates, multipart messages, and other REST capabilities.
Properties
Action Type
Sets the kind of HTTP action to perform against the REST service. Valid actions include GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE.
Base URL
Sets the base URL that defines how the REST service is accessed and used.
Query Parameters
Sets the optional input string data that are used as query parameters to the REST service.
Request Content Type
Sets the optional “Content-Type” header in the HTTP request to the REST service. Typical content types include “text/plain” and “text/xml”.
Request Entity
Sets the optional request entity to be sent with an HTTP POST or PUT action.
Response Type
Sets the type of the response from the REST service.
The RestAction API has two variants:
public void setXpathResponseType(Class xpathResponseType);
which is used in Java APIs; and
public void setXpathResponseTypeAsString(String xpathResponseType);
Which is used in the Designer.
Username and Password
Sets the optional password used to access the REST service, assuming the service is secured with basic authentication.
Preemptive Authentication
Sets whether the client should send an authentication request even before the server gives a 401 response.
Interactive Authentication
Sets whether the client should interactively prompt for credentials should it receive a 401 response.
XPath Expression
Sets the optional XPath expression used to query the response from the REST service.
XML Namespaces
Sets the optional XML namespaces for resolving an XPath query. The key to the map is the namespace prefix. The corresponding value is the target namespace.
XPath response type
Sets the optional type of the response from an XPath query.
SSL
Sets whether the client should use SSL for communication.
Body Parts
Sets the body parts, commonly called file attachments, that are set in a multipart HTTP request to the REST service. The key to each property is the name of the body part. The corresponding value is a filename that references the contents of that body part.
HTTP Headers
Sets the optional headers set in the HTTP request to the REST service. Typical headers include “User-Agent: Flux Scheduler/7.10”. The User-Agent header contains information about the user agent originating the request.
Results
The Rest Action returns its results in the flow context variable “result”. These results include the response code and status from the server, as well as response type metadata:
| Flow Context Variable | Field | Java Type | Description | Prescript / Postscript Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RESULT | responseCode | int | The HTTP response code from the server after invoking the REST service. | int responseCode = flowContext.get("RESULT").responseCode; System.out.println("Response code: " + responseCode); |
| RESULT | responseStatus | String | The HTTP response status from the server after invoking the REST service. | String responseStatus = flowContext.get("RESULT").responseStatus; | System.out.println("Response status: " + responseStatus); |
| RESULT | result | Object | The object returned from the REST service call. | Object result = flowContext.get("RESULT").result; | System.out.println("Result: " + result); |
| RESULT | type | String | The HTTP media type of the object contained in the “result” field. | String type = flowContext.get("RESULT").type; System.out.println("Response type: " + type); |
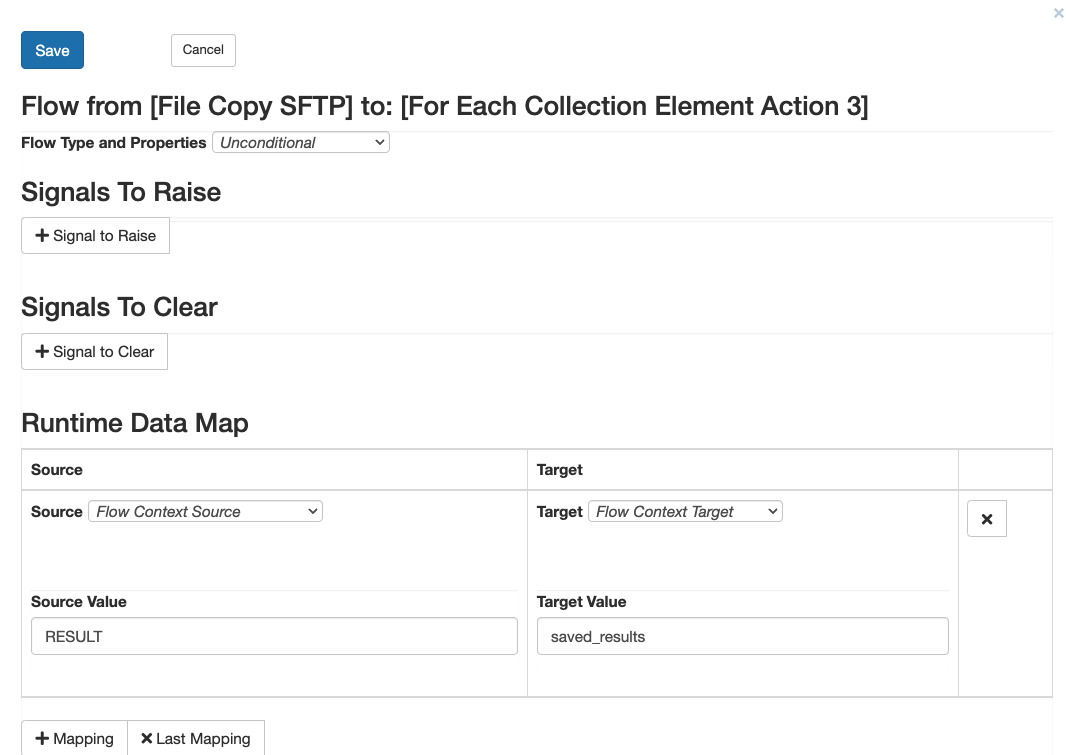
Passing Results with a Runtime Data Map
You can use a Runtime Data Map to copy one of the result fields into a new variable (for future reference or to reuse the data later in the workflow).
You can save the results into a new variable like so: